Basic
Chemistry
Atoms are the basic unit of chemistry.
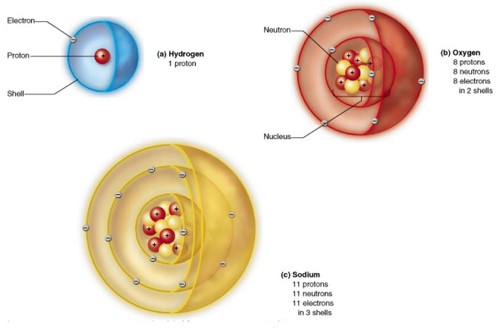
The human body is made up of a couple
dollars worth of chemicals.
Sometimes atoms gain or lose electrons. These are ions:
Here are some examples:
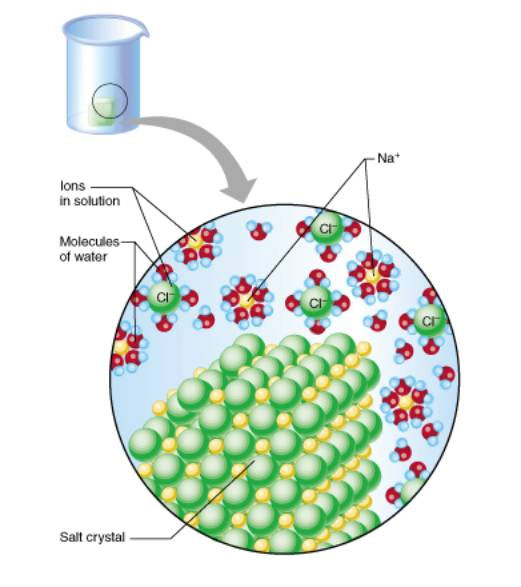
Na+ Sodium
K+ Potassium
Cl- Chloride
Ca+ Calcium
Fe+ Iron
P- Phosphorous
Hooking Stuff Together:
Chemical Bonds
,Covalent - electron sharing
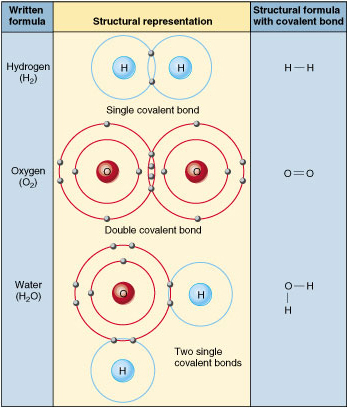
,Ionic - gain or lose
electron (opposites attract)
,Hydrogen - weakest
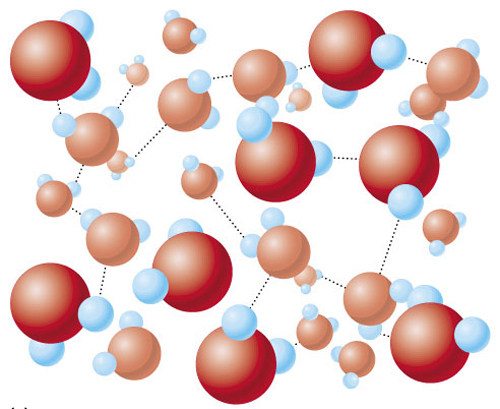
Properties of water:
,Unequal covalent bonding - partial charges
,Polar vs. Nonpolar compounds
,Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic
In some cases, weaker bonds can overcome
stronger bonds
(salt or sugar dissolves in water)
Saturation
pH
Acids vs. Bases
Measure of H+ ions in solution
, Water (H2O) splits into H+ and OH-
, When have equal parts (1:1 ratio) pH is
neutral (7)
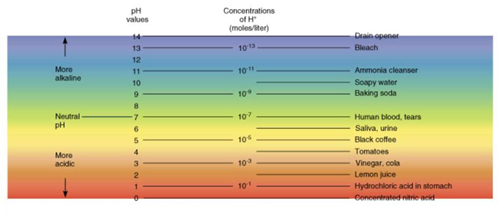
Acids add
H+ to solution
, HCl splits into H+ and Cl-
, Extra H+ means acid solution (no more
equal parts)
Bases add OH- to solution
, NaOH splits into Na+ and OH-
, Extra OH- shifts ratio (fewer free H+
than normal)
Basic Chemistry
Atoms are the basic unit of chemistry.
The human body is made up of a couple dollars
worth of chemicals.
Sometimes atoms gain or lose electrons.
These are ions:
Here are some examples:
Na+
Sodium
K+
Potassium
Cl-
Chloride
Ca+
Calcium
Fe+
Iron
P-
Phosphorous
Hooking Stuff Together: Chemical Bonds
Covalent - electron sharing
Ionic - gain or lose electron (opposites attract)
Hydrogen - weakest
Properties of water:
Unequal covalent bonding - partial charges
Polar vs. Nonpolar compounds
Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic
In some cases, weaker bonds can overcome
stronger bonds
(salt or sugar dissolves in water)
Saturation
pH
Acids vs. Bases
Measure of H+ ions in solution
, Water (H2O) splits into H+ and OH-
, When have equal parts (1:1 ratio) pH is
neutral (7)
Acids add H+ to solution
, HCl splits into H+ and Cl-
, Extra H+ means acid solution (no more
equal parts)
Bases add OH- to solution
, NaOH splits into Na+ and OH-
, Extra OH- shifts ratio (fewer free H+
than normal)
Organic Compounds
Organic vs. Inorganic
Cells are made from 4 basic compounds
,Carbohydrates
,Lipids
,Proteins
,Nucleic Acids
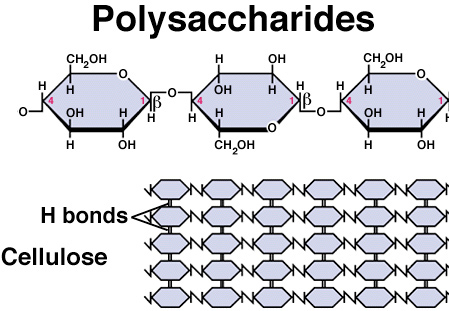
Carbohydrates:
, 5 or 6 Carbon rings
, Can hook these together
get disaccharides or polysaccharides
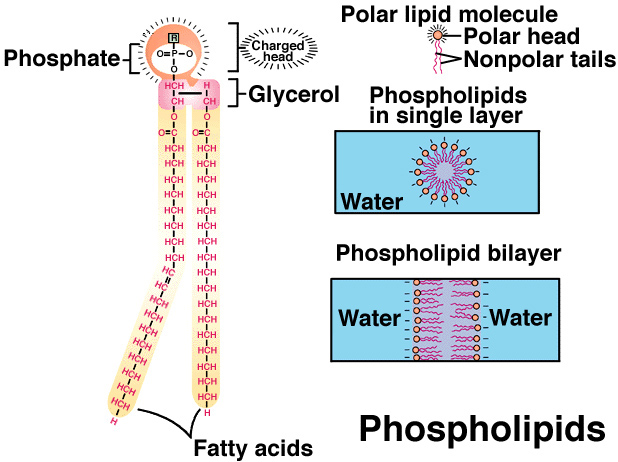
Lipids
,Fatty acids long Carbon chains (name depends
on # of carbons)
,Triglyceride - 3 fatty acids linked by glycerol
,Steroids also in this group
,Phospholipid - remove 1 fatty acid and add a Phosphorous
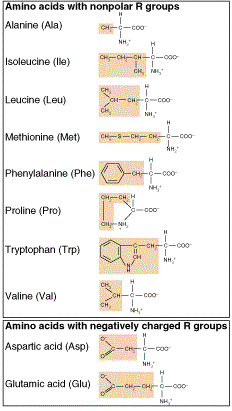
Proteins
Long chains of amino acids
NH2 - C - COOH
, R side chain is attached to central Carbon
, 20 different types of side chains (20
amino acids)
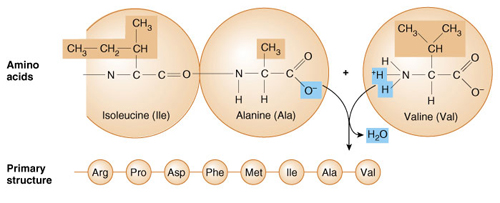
Linked together by Peptide
bonds
Many amino acids are linked together
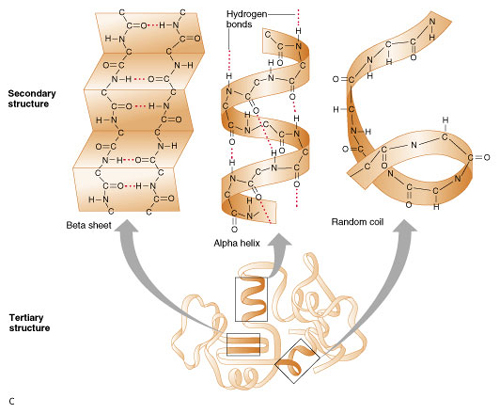
Levels
of protein structure
,Primary - exact sequence
,Secondary - simple structures
,Tertiary - complex 3D structures
,Quarternary - multiple subunits
Quarternary structure: multiple
subunits forming larger structure
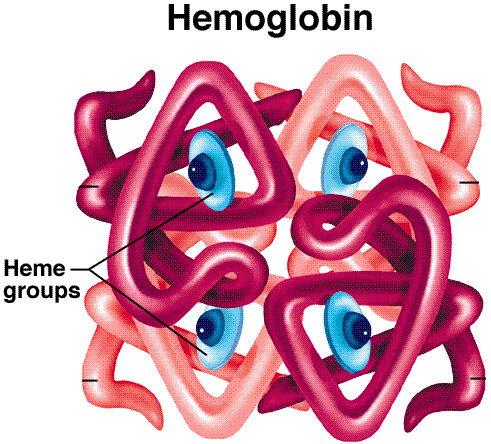
Proper protein function depends
on correct 3D structure.
Especially important for enzyme activity
these accelerate chemical reactions
vital to proper cell function
defects; sickle cell, cystic fibrosis
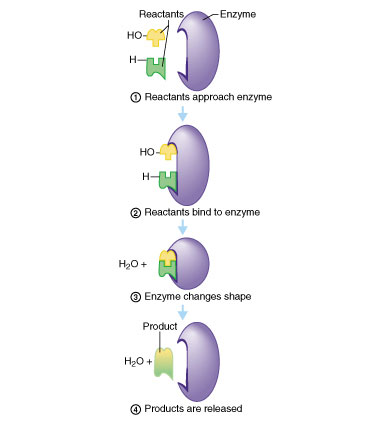
Nucleic
Acids
3 Parts
,Carbohydrate
,Base (one of five)
,Phosphorous
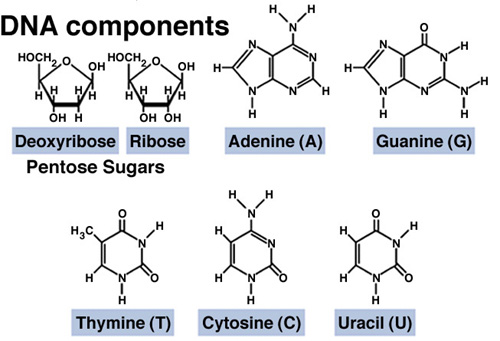
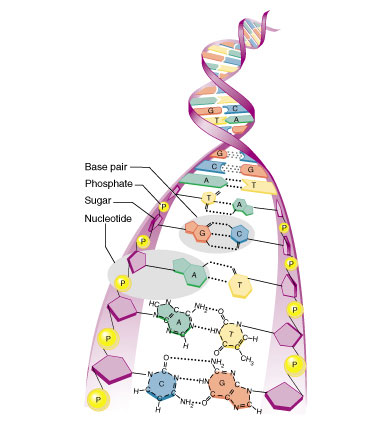
Making
DNA chains
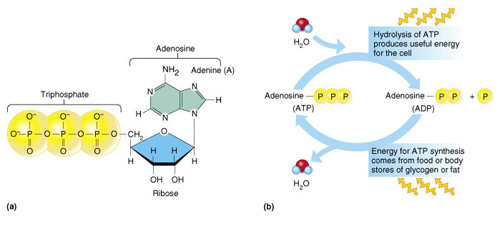
ATP
|
